
Generative AI vs Traditional AI: Key Differences
Oct 22, 2024 5 Min Read 3343 Views
(Last Updated)
The world is now filled with Artificial Intelligence right from your Google Maps to your voice assistant, AI is everywhere in every possible way.
There are different types of AI and one important type among all the others is Generative AI. Now, what’s the difference between generative AI and traditional AI? The answer to this question as well as a solution to the debate on generative AI vs traditional AI will be there in this article.
We’ll be covering key differences such as their applications, complexity, adaptability, and even cost and scalability. So, without further ado, let us get started!
Table of contents
- What is Generative AI and Traditional AI?
- Generative AI vs Traditional AI: Understanding the Key Differences
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- What is the main difference between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
- How do Generative AI and Traditional AI approach data processing?
- How are the applications for Generative AI different from those for Traditional AI?
- What are the key advantages of using Generative AI?
- How does the development process differ between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
- What are some real-world examples of Generative AI and Traditional AI?
- What are the data requirements for Generative AI and Traditional AI?
What is Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Before seeing the key difference between generative AI and traditional AI, the first major difference lies in their definition, so let us have a look at it.
Generative AI is a type of AI model that has the capability to produce its own texts, images, music, and even videos that have not existed before. It does so by the user providing proper prompts.
On the other hand, traditional AI is a set of AI models that are predesigned to perform a specific task by following a set of guidelines and patterns. These are majorly helpful in classification, prediction, and optimization. It cannot create or generate new content as Generative AI does effortlessly.
If you are intrigued by the working nature of Generative AI and want to learn more about it, consider enrolling in GUVI’s Self-paced Generative AI course that provides you with all the necessary knowledge along with a certificate!
Generative AI vs Traditional AI: Understanding the Key Differences
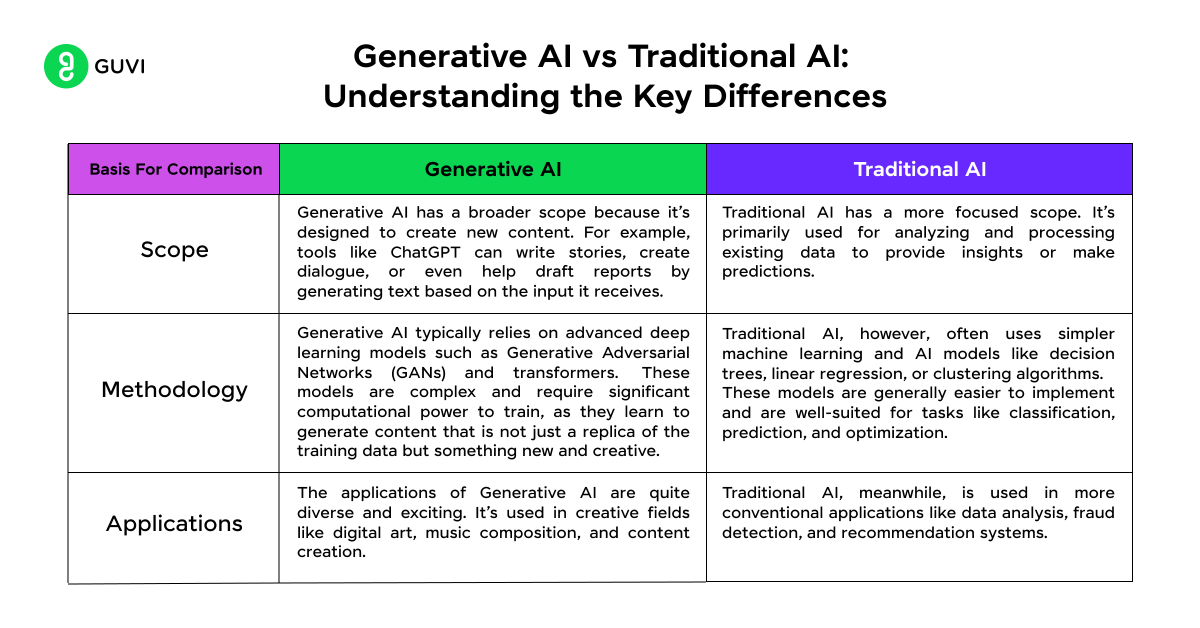
Now that the basic definition of both AI technology has been covered, let us move on to our key differences between generative AI and traditional AI.
| S. No. | Basis For Comparison | Generative AI | Traditional AI |
| 1 | Scope | Generative AI has a broader scope because it’s designed to create new content. For example, tools like ChatGPT can write stories, create dialogue, or even help draft reports by generating text based on the input it receives. | Traditional AI has a more focused scope. It’s primarily used for analyzing and processing existing data to provide insights or make predictions. |
| 2 | Methodology | Generative AI typically relies on advanced deep learning models such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformers. These models are complex and require significant computational power to train, as they learn to generate content that is not just a replica of the training data but something new and creative. | Traditional AI, however, often uses simpler machine learning and AI models like decision trees, linear regression, or clustering algorithms. These models are generally easier to implement and are well-suited for tasks like classification, prediction, and optimization. |
| 3 | Applications | The applications of Generative AI are quite diverse and exciting. It’s used in creative fields like digital art, music composition, and content creation. | Traditional AI, meanwhile, is used in more conventional applications like data analysis, fraud detection, and recommendation systems. |
| 4 | Complexity | Generative AI is generally more complex than Traditional AI. The models involved require significant expertise to develop and fine-tune. | Traditional AI models are usually less complex, focusing more on data processing and pattern recognition rather than creating new data. |
| 5 | Training Data Requirements | Generative AI typically requires vast amounts of diverse data to function effectively. The more varied and extensive the dataset, the better the AI can learn to generate unique content. | Traditional AI, however, can often perform well with smaller, more specific datasets. It’s focused more on recognizing patterns and making predictions within the bounds of the data it has been trained on. |
| 6 | Performance Metrics | The performance of Generative AI is often evaluated based on the creativity and quality of its output. This could mean how realistic or innovative the generated content appears to human users. | Traditional AI, on the other hand, is usually judged by more general metrics like accuracy, precision, and recall. These metrics measure how well the AI model can classify data, predict outcomes, or recognize patterns based on the input it receives. |
| 7 | Resource Intensity | Generative AI is a model that requires high resource intensity, often requiring significant computational power, especially during the training phase. This includes using high-end GPUs or TPUs, which can drive up costs and make development more challenging. | Traditional AI, while still demanding, typically requires fewer resources compared to gen AI. Many traditional AI models can be trained and deployed on more modest hardware. |
| 8 | Output | The output from Generative AI is new and original. This contrasts with Traditional AI, which processes existing data to provide insights or predictions. | The output of Traditional AI is usually a classification, a recommendation, or a prediction based on the patterns it has learned from the data. |
| 9 | User Interaction | Gen AI relies on user prompts. That means, the user interaction is heavy compared to traditional AI. This interactive nature makes it particularly useful in creative industries, where users can explore different possibilities with AI. | Traditional AI, however, typically operates more in the background. It processes data and delivers results without much need for user input, which is ideal for tasks like automation and analysis. |
| 10 | Adaptability | Generative AI is highly adaptable, as it can learn and evolve in creative ways. It can generate increasingly sophisticated content as it continues to learn from new data. | Traditional AI is less adaptable, as it usually follows predefined rules and is focused on improving within a specific domain. |
| 11 | Deployment | Deploying Generative AI can be more challenging due to the specialized infrastructure and resources it requires. | Traditional AI, on the other hand, has more established and straightforward deployment methods. These models are often easier to integrate into existing systems. |
| 12 | Ethical Considerations | Generative AI raises significant ethical concerns, particularly regarding the potential misuse of AI-generated content. This includes deepfakes, fake news, and other forms of content that could be misleading or harmful. | Traditional AI’s ethical considerations are usually centered around data privacy and bias in decision-making processes, which, while important, tend to be less controversial in terms of content creation. |
| 13 | Real-World Examples and Tools | Some well-known examples of Generative AI include tools like DALL-E, which can generate detailed images from textual descriptions, and ChatGPT, which can write essays, stories, and more. Other Gen AI tools include Gemini, Synthesia etc., | Traditional AI is used majorly by applications like spam filters that detect and block unwanted emails, and recommendation systems that suggest products or content based on your past behavior. Tools include voice assistants like Siri and Alexa. |
| 14 | Innovation Potential | The innovation potential of Generative AI is very high. It opens up new possibilities in creative fields, allowing for the generation of content that was previously unimaginable. | Traditional AI, while still innovative, tends to focus on incremental improvements and optimizations within existing systems. It’s more about making processes more efficient rather than creating something entirely new. |
| 15 | Cost | The cost associated with Generative AI is generally higher due to the need for advanced hardware and extensive training data. This can make it a more expensive option, especially for businesses looking to experiment with cutting-edge AI technologies. If we take ChatGPT for instance, the premium model costs around 1600 INR per month which is too expensive for public usage whereas Traditional AI comes free of cost. | Traditional AI is fully free or often has a lower cost barrier, as it can utilize existing technologies and infrastructure, making it more feasible for a wider range of applications. We use traditional AI on a daily basis without even knowing. For instance, the Google voice assistant in our mobiles are totally free yet provides a dedicated AI service. |
| 16 | Scalability | Scaling Generative AI can be challenging due to the resource demands and complexity of the models. However, once scaled, it can offer highly personalized and creative outputs at a large scale. | Traditional AI, on the other hand, is easier to scale, particularly with the help of cloud computing. |
| 17 | User Base | The user base for Generative AI is rapidly growing, particularly in creative industries such as digital art, media, and entertainment. | Traditional AI has a more established user base across various corporate sectors, including finance, healthcare, and logistics, where its analytical capabilities are highly valued. |
| 18 | Learning Curve | The learning curve for Generative AI is more narrow and tough, as it requires understanding advanced concepts like deep learning and neural networks. This can be a barrier for those new to AI. | Traditional AI has a more gradual learning curve, making it more accessible for beginners who are familiar with basic algorithms and data processing techniques. |
| 19 | Community and Support | The community and support for Generative AI are still emerging as it is a new technology, with new forums and resources being created as the technology develops. | Traditional AI, however, benefits from a well-established community with extensive resources, including documentation, tutorials, and forums, making it easier to find help and collaborate. |
| 20 | Future Trends | Generative AI is at the right place with numerous innovations with the potential to revolutionize various industries by enabling new forms of content creation and interaction. | Traditional AI will likely continue to grow steadily, focusing on optimizing existing processes and improving accuracy and efficiency in data-driven decision-making. |
In case, you want to explore more generative AI and traditional AI, consider enrolling for GUVI’S AIML Course which teaches everything related to it with an industry-grade certificate!
Conclusion
In conclusion, the key differences between generative AI and traditional AI have been laid out in a clear and straightforward manner. Generative AI is the creation of a new world from nothing, while Traditional AI is more of making the already existing processes more efficient.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a professional, or just someone curious about the future of AI, knowing the differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI is key to understanding the ever-changing world of AI.
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
The main difference is that Generative AI creates new content, while Traditional AI analyzes and processes existing data.
2. How do Generative AI and Traditional AI approach data processing?
Generative AI generates new data based on patterns it has learned, whereas Traditional AI processes and interprets existing data to make predictions or decisions.
3. How are the applications for Generative AI different from those for Traditional AI?
Generative AI is used in creative tasks like content creation, while Traditional AI is used in data-driven tasks like predictions, classifications, and optimizations.
4. What are the key advantages of using Generative AI?
Generative AI excels at creating new original content and offers high innovation potential in creative industries.
5. How does the development process differ between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Generative AI development is more complex, requiring advanced models and more computational resources, while Traditional AI development is generally simpler and more resource-efficient.
6. What are some real-world examples of Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Examples of Generative AI include GPT-4 and DALL-E, while Traditional AI includes spam filters and recommendation systems.
7. What are the data requirements for Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Generative AI requires large, diverse datasets for training, while Traditional AI can often work with smaller, more specific datasets.

























Did you enjoy this article?