
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI: A Comprehensive Guide
Dec 21, 2024 7 Min Read 6587 Views
(Last Updated)
As we stand on the brink of technological revolutions, artificial intelligence (AI) emerges as a beacon of innovation, propelling forward with an array of advancements that redefine the essence of how businesses operate and how daily human activities are conducted.
The exploration into the advantages and disadvantages of AI uncovers a panorama of benefits and challenges, illuminating both its prowess in enhancing efficiency and transparency, and its potential drawbacks, including concerns of unemployment and the ethical implications of its widespread implementation.
Understanding the dual facets of AI is crucial for harnessing its full potential while mitigating the adverse effects it may harbor on society and the economy.
This comprehensive guide aims to help you learn about AI and its intricacies, including the foundational algorithms and principles of machine learning that fuel its capabilities.
Table of contents
- 1) What is Artificial Intelligence?
- 1) Understanding AI and Its Core Components
- 2) The Evolution and Impact of AI Technologies
- 3) Ethical Considerations in AI
- 2) How Does AI Work?
- 1) Understanding the Mechanisms of AI
- 2) Training and Learning in AI
- 3) Data Analysis and Prediction
- Advantages and Disadvantages of AI
- 3) Advantages of AI
- 1) Reduction in Human Error
- 2) Takes Risks in Place of Humans
- 3) Available 24/7
- 4) Facilitates Faster Decision-Making
- 5) AI in Daily Applications
- 4) Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
- 1) High Costs of Creation
- 2) Potential Increase in Unemployment
- 3) Lack of Creativity and Emotion
- 4) Ethical Concerns
- 5) Dependency and Reliability Issues
- 5) Applications of AI in Different Sectors
- 1) Healthcare
- 2) Finance
- 3) Customer Service
- 4) Manufacturing
- 6) The Future of Artificial Intelligence
- 1) Predicted Advancements
- 2) AI and Human Collaboration
- 3) Addressing Potential Risks
- Takeaways...
- FAQs
- What are the benefits of artificial intelligence?
- How AI is useful in our life?
- What is AI used for today?
- Who is the father of AI?
1) What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative branch of computer science that is reshaping how we interact with technology and the world around us.
At its core, AI involves machines performing tasks that typically require human intelligence.
These tasks range from simple ones, like recognizing speech, to complex ones, such as driving cars or simulating human conversation.
1.1) Understanding AI and Its Core Components
- AI systems are built on the pillars of learning, reasoning, and self-correction.
- This involves the creation and implementation of algorithms that enable machines to process data, learn from it, and make decisions or predictions based on that learning.
- The sophistication of these systems can vary significantly, from basic automation capabilities to advanced systems that can improve their performance over time without human intervention.
Table: Key Components of AI
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Learning | Acquiring data and transforming it into actionable knowledge. |
| Reasoning | Applying rules to reach conclusions or make predictions. |
| Self-correction | Adjusting actions based on new data to improve accuracy. |
1.2) The Evolution and Impact of AI Technologies
- AI has evolved dramatically since its inception. Early AI was focused on performing specific tasks, such as playing chess or simple speech recognition.
- However, modern AI, powered by advancements in machine learning and deep learning, is capable of learning from vast amounts of data and making decisions with minimal human oversight.
- Generative AI, a recent breakthrough, extends AI’s capabilities to create content, such as text, images, and music, that is indistinguishable from that created by humans.
- This leap in AI capabilities is largely driven by improvements in natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision.
1.3) Ethical Considerations in AI
- As AI becomes more integrated into daily life and critical industries, the discussion around AI ethics grows.
- It is crucial to consider how AI is used and the potential societal impact of its decisions.
- Ensuring AI is developed and implemented responsibly is paramount to harness its benefits while minimizing risks such as privacy invasion, unemployment due to automation, and decision-making biases.
- AI continues to be a field of dynamic growth and immense potential.
- Understanding its mechanisms, applications, and implications is essential for leveraging its capabilities responsibly and effectively in our increasingly digital world.
Before moving forward, make sure you understand the basics of Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning, including algorithms, data analysis, and model training. If you want to learn more, join GUVI’s AI & Machine Learning Courses with job placement assistance. You’ll discover important tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, scikit-learn, and others.
Plus, you’ll work on real projects to gain practical experience and improve your skills in this fast-growing field.
2) How Does AI Work?
2.1) Understanding the Mechanisms of AI
Artificial Intelligence operates fundamentally through machine learning, essentially teaching computers to perform tasks by exposing them to numerous examples.
This allows the computer to learn from these examples and begin identifying patterns within the data.
Table: Basic AI Learning Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Acquisition | Gathering diverse and extensive data sets that serve as the foundation for learning. |
| Pattern Recognition | Algorithms analyze the data to identify and learn from patterns. |
| Refinement | Continuous improvement of algorithms based on new data to enhance accuracy and performance. |
2.2) Training and Learning in AI
The training of AI involves a detailed and structured process where algorithms are fed data, and through iterative adjustments, they enhance their accuracy and decision-making capabilities.
This is akin to teaching a child through repeated examples and corrections.
Machine Learning Types
- Supervised Learning: The AI is trained on a labeled dataset, learning to make predictions based on the provided answers.
- Unsupervised Learning: The AI explores unlabeled data to discover hidden patterns and structures without prior examples.
- Reinforcement Learning: Similar to training a pet with rewards, the AI learns from consequences of its actions, optimizing its decisions for better outcomes over time.
Deep Learning, a subset of machine learning, mimics the human brain’s structure through layers of nodes or neurons, allowing the AI to process data in complex, layered manners.
This architecture is crucial for tasks that require a deep understanding of data, such as image and speech recognition.
2.3) Data Analysis and Prediction
AI’s ability to analyze data and make predictions is pivotal. It uses sophisticated algorithms to sift through large datasets, identifying patterns that humans might overlook.
This capability is enhanced by the AI’s ability to learn from the data it processes, constantly improving its accuracy and reliability.
Table: AI Data Analysis Techniques
| Technique | Application |
|---|---|
| Machine Learning | Automates the identification of data patterns, improving over time with more data exposure. |
| Neural Networks | Processes data through layers, extracting complex features for detailed analysis. |
| Predictive Analytics | Uses historical data to forecast future trends, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making. |
AI systems continuously refine their algorithms through feedback loops, comparing their outputs with expected results and adjusting accordingly.
This iterative learning process ensures that AI systems remain effective and accurate in their tasks, adapting to new data and scenarios seamlessly.
By understanding these core functionalities, you can appreciate how AI works not just as a technological tool but as a dynamic and evolving field that mirrors some aspects of human learning and adaptation.
Also Read: Best Product-Based Companies for AI Engineers in 2025
Advantages and Disadvantages of AI
3) Advantages of AI
3.1) Reduction in Human Error
- One of the significant advantages of artificial intelligence is its ability to minimize human error, enhancing accuracy across various applications.
- AI systems are designed to execute tasks with high precision based on pre-defined algorithms and data.
- This capability is particularly beneficial in fields like data analytics, where AI can detect and correct errors that humans might overlook, such as typos, misalignments, or incorrect data entries.

Table: Examples of AI Reducing Human Error
| Sector | Application of AI |
|---|---|
| Data Entry | Automates correction of data entry errors. |
| Financial Analysis | Enhances accuracy in financial forecasting and reporting. |
| Healthcare | Reduces diagnostic errors by analyzing medical data. |
3.2) Takes Risks in Place of Humans
- AI can be deployed in environments that are too dangerous for humans, such as radioactive sites, deep-sea exploration, or disaster zones.
- By using robots and AI systems, we can avoid human casualties and conduct research or rescue operations effectively.
- This not only ensures the safety of human workers but also expands the scope of exploration and data collection in environments that were previously inaccessible.
3.3) Available 24/7
- Unlike humans, who need breaks and have limited working hours, AI systems can operate continuously without fatigue.
- This round-the-clock availability makes AI invaluable in industries requiring constant attention, such as customer service or surveillance.
- AI-powered chatbots can interact with customers, handle queries, and resolve issues at any time of the day, significantly improving service availability and customer satisfaction.

Table: AI Applications in 24/7 Operations
| Industry | Application of AI |
|---|---|
| Customer Service | AI chatbots handle inquiries and support around the clock. |
| Manufacturing | Continuous production and monitoring processes. |
| Healthcare | Patient monitoring and emergency response systems. |
3.4) Facilitates Faster Decision-Making
- AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data at incredible speeds allows for quick decision-making which is essential in many sectors.
- In finance, AI can analyze market data to make real-time trading decisions. In healthcare, AI assists in making faster diagnoses based on medical imaging and patient data.
- This speed and efficiency in decision-making can greatly enhance productivity and effectiveness across fields.
3.5) AI in Daily Applications
- Daily applications of AI are becoming more ingrained in our lives, from personalized recommendations on streaming services to enhancing security through facial recognition technologies.
- AI improves user experiences by analyzing personal preferences and behaviors, making interactions more tailored and efficient.
- In transportation, AI optimizes routes and traffic management, reducing commute times and enhancing safety.
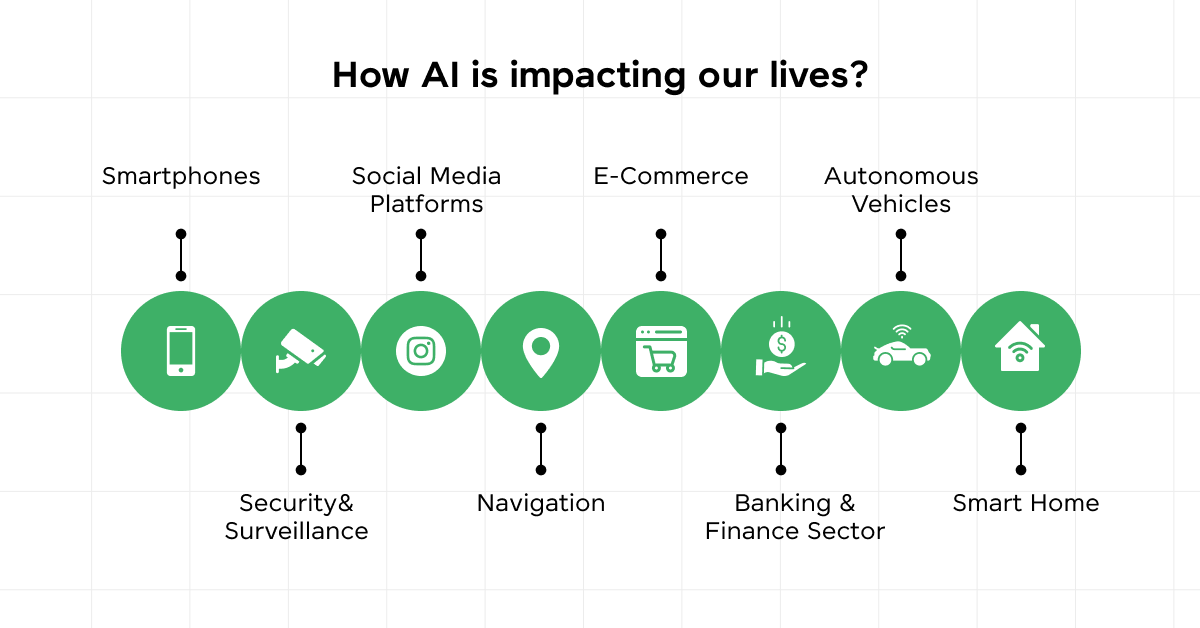
Table: Daily Applications of AI
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Personalized Media | AI curates content based on user preferences. |
| Security | Facial recognition for secure access to devices and facilities. |
| Transportation | AI-driven route optimization and traffic management. |
By integrating these AI capabilities, we can leverage technology to reduce risks, increase availability, accelerate decision-making, and enhance daily operations, making AI a transformative force across various sectors.
Must Read: 21 Best AI Tools For UI/UX Designers in 2025
4) Disadvantages of Artificial Intelligence
4.1) High Costs of Creation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) systems require substantial financial investment, not only in the initial development phase but also in ongoing maintenance and upgrades.
- The advanced hardware needed for training AI models, such as GPUs and specialized AI processors, can be prohibitively expensive.
- Additionally, the cost of acquiring and processing large datasets, which are crucial for training AI algorithms, adds to the overall expense. Here’s a breakdown of some typical costs associated with AI development:
Table: Estimated Costs for AI Development Components
| Component | Cost Estimate | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Hardware (GPUs, TPUs) | $10,000 – $100,000 per unit | Essential for processing large datasets |
| Data Acquisition | Varies widely | Costs increase with data volume and complexity |
| Software Development | $100,000 – $1,000,000+ | Depending on the complexity of the AI applications |
| Maintenance & Updates | 20-30% of initial project cost | Annual costs for keeping the AI up-to-date |
4.2) Potential Increase in Unemployment
- AI’s ability to automate tasks can lead to significant job displacement, particularly in sectors where routine tasks are prevalent.
- Studies suggest that a substantial percentage of jobs could be at risk due to automation technologies like AI.
- This shift could exacerbate socioeconomic disparities and necessitate significant investments in retraining programs.

Table: Job Risk Estimates from AI Automation
| Job Sector | Risk Percentage | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Up to 50% | High risk of job displacement |
| Retail | 30-40% | Moderate to high risk |
| Professional Services | 20-30% | Lower risk, but still significant |
4.3) Lack of Creativity and Emotion
- AI systems, while powerful, lack the emotional intelligence and creativity that humans bring to many professional and creative endeavors.
- They operate based on algorithms and data, without the capacity for empathy or the intuitive leaps that often drive innovation and artistic expression.
- This limitation is particularly evident in fields that rely heavily on interpersonal skills and emotional sensitivity, such as counseling, customer service, and creative arts.

4.4) Ethical Concerns
- The deployment of AI raises a multitude of ethical issues, from privacy concerns to the potential for bias in decision-making processes.
- AI systems can inadvertently perpetuate existing biases present in their training data, leading to unfair outcomes in areas such as hiring, law enforcement, and loan approvals.
- Furthermore, the use of AI in surveillance and data collection poses significant risks to individual privacy and freedoms.
Table: Ethical Challenges in AI
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Privacy | Potential for misuse of personal information |
| Decision-making Bias | AI may replicate societal biases in its algorithms |
| Surveillance | Increased monitoring capabilities can infringe on privacy |
4.5) Dependency and Reliability Issues
- Over-reliance on AI can make individuals and organizations vulnerable to unexpected failures or errors in AI systems.
- These systems, while robust, can still malfunction or deliver incorrect outputs, which may not be immediately noticeable, leading to significant consequences.
- Ensuring that AI systems are reliable and that there are contingencies in place is critical, especially in sectors where safety and precision are paramount.
By understanding these disadvantages, stakeholders can better prepare for and mitigate the negative impacts of AI, ensuring that its deployment is both responsible and beneficial for society as a whole.
5) Applications of AI in Different Sectors
5.1) Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing healthcare by enhancing diagnostic accuracy, optimizing treatment plans, and improving patient outcomes.
AI’s capability to analyze vast datasets allows for more precise diagnostics and personalized treatment approaches, significantly advancing areas like radiology and oncology.
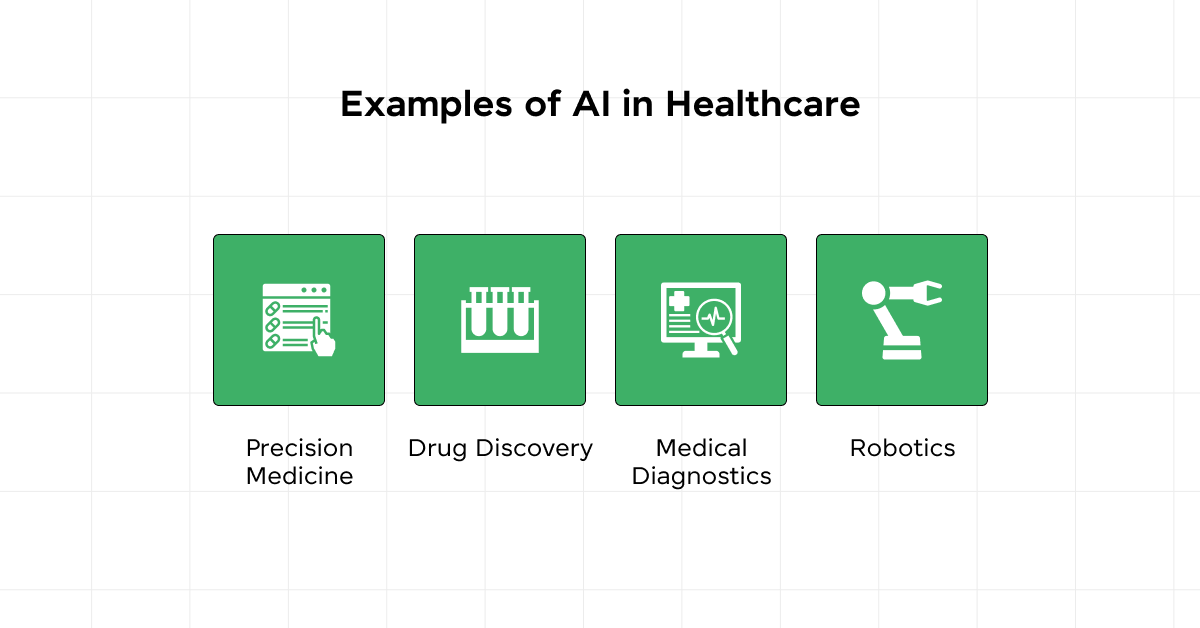
Table: AI Applications in Healthcare
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Diagnostic Accuracy | AI algorithms assist in diagnosing diseases with higher precision. |
| Treatment Personalization | AI analyzes patient data to tailor treatments to individual needs. |
| Patient Monitoring | AI tools monitor patient health in real-time, improving care responsiveness. |
5.2) Finance
In the financial sector, AI is a powerful tool for risk management, fraud prevention, and customer personalization.
Financial institutions are leveraging AI to analyze customer data for better service delivery and to enhance security measures.
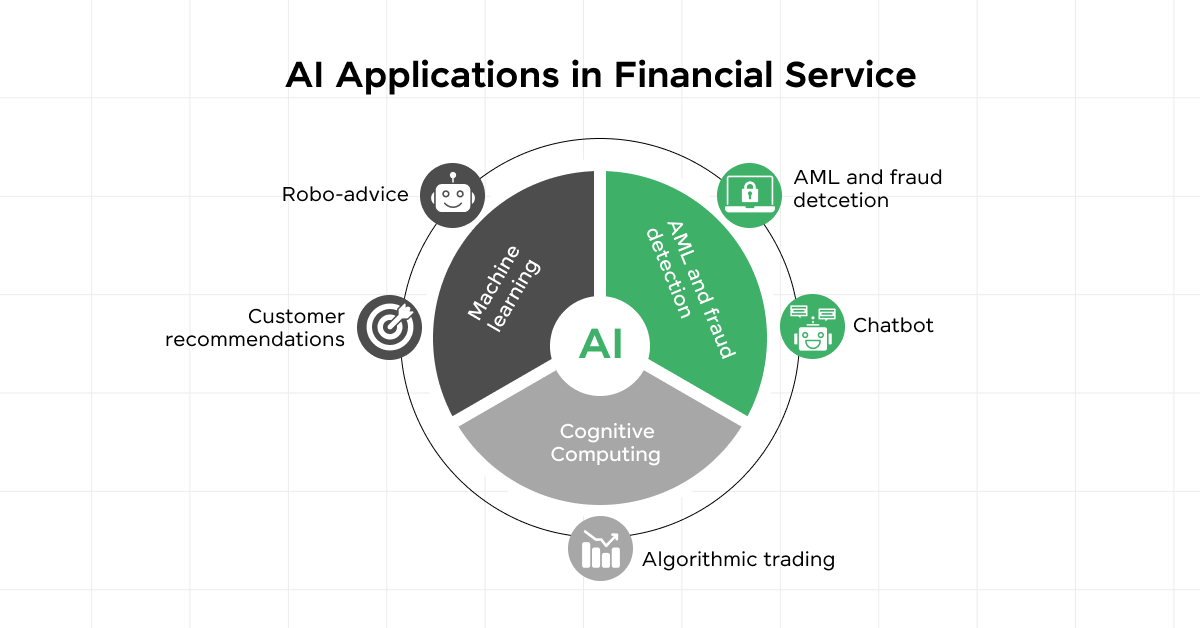
Table: AI Impact on Finance
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Management | AI evaluates investment risks and assists in making informed decisions. |
| Fraud Prevention | AI detects unusual patterns, helping prevent fraudulent activities. |
| Customer Insight | AI personalizes banking experiences by analyzing user behavior. |
5.3) Customer Service
AI enhances customer service by automating responses and providing personalized service through chatbots and virtual assistants.
These AI-driven tools are available 24/7, ensuring that customer inquiries are handled efficiently regardless of the time.
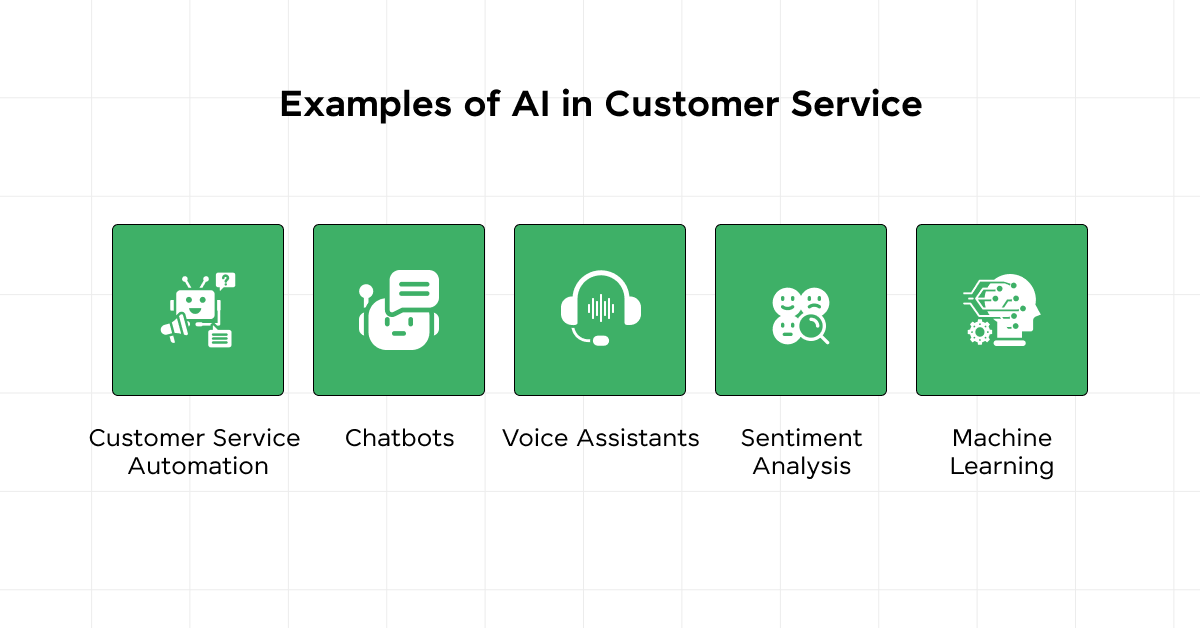
Table: AI Enhancements in Customer Service
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| 24/7 Availability | AI tools respond to customer queries at any time, improving accessibility. |
| Personalization | AI analyzes past interactions to tailor responses to individual preferences. |
5.4) Manufacturing
AI is transforming manufacturing with smart automation, predictive maintenance, and optimized production processes.
AI-driven systems streamline operations, reduce downtime, and enhance product quality through precise quality control measures.
Table: AI Applications in Manufacturing
| Process | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Production Optimization | AI algorithms fine-tune manufacturing processes for efficiency. |
| Quality Control | AI systems detect defects and inconsistencies in real-time. |
| Maintenance Prediction | AI predicts equipment failures, reducing unexpected downtimes. |
AI’s diverse applications across different sectors not only streamline operations but also enhance decision-making and service delivery, proving its indispensable role in modern industry.
Also Explore: AI Video Revolution: How the Internet is Forever Changed [2025]
6) The Future of Artificial Intelligence
6.1) Predicted Advancements
The trajectory of artificial intelligence (AI) suggests a future where its integration into daily life and industry is ubiquitous.
By 2030, it is anticipated that AI will not only act as personal assistants, tutors, and career counselors but will also play critical roles in strategic decision-making across various sectors.
The market dynamics are expected to shift significantly, with companies like Nvidia already showing a substantial lead in market capitalization compared to traditional tech giants like Intel.
Table: Market Predictions for AI Companies
| Company | Market Cap | Predicted 2030 Market Cap |
|---|---|---|
| Nvidia | $2.2 trillion | Significant increase |
| Intel | $186 billion | Narrowing gap with Nvidia |
6.2) AI and Human Collaboration
The synergy between AI and human creativity is poised to usher in a new era of innovation.
AI’s capacity for data analysis and pattern recognition complements human intuition and emotional intelligence, enhancing creativity and problem-solving in fields ranging from art to science.
This collaboration is expected to break new ground in creating solutions for pressing global challenges such as climate change and healthcare.

Table: Benefits of AI and Human Collaboration
| Sector | Benefits of Collaboration |
|---|---|
| Arts | Enhanced creativity through AI-driven data analysis |
| Science | Innovative solutions for complex problems combining AI and human insight |
| Healthcare | Improved diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans |
6.3) Addressing Potential Risks
As AI technologies advance, they bring potential risks that need careful management. Ethical concerns, job displacement, and privacy issues are at the forefront of challenges that must be addressed.
Strategies such as adaptive regulation, international collaboration, and public education are crucial for mitigating these risks.
Additionally, the development of AI ethics frameworks and the implementation of safety measures will be vital to ensure that AI benefits society without causing unintended harm.
Table: Strategies for Mitigating AI Risks
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Adaptive Regulation | Regulations that evolve with AI advancements |
| International Collaboration | Global efforts to ensure safe and ethical AI use |
| Public Education | Increasing awareness about AI capabilities and risks |
By understanding these dynamics, you can better prepare for a future where AI is a pervasive part of life and business, offering tremendous benefits while posing manageable risks.
Begin your Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning journey with GUVI’s Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Courses. Learn essential technologies like Matplotlib, Pandas, SQL, NLP, and deep learning while working on real-world projects.
Takeaways…
Navigating through the complexities and advancements of artificial intelligence, we have delved into both its promising potentials and the challenges it presents.
A balanced perspective is crucial for leveraging AI’s benefits while addressing its limitations and societal impacts thoughtfully.
As we stand at the threshold of AI’s future, it is clear that its evolution will continue to shape our world in profound ways.
The collaborative potential between AI and human intelligence holds the promise of groundbreaking advancements in creativity, problem-solving, and innovation.
Also Explore: Generative AI vs Predictive AI: A Comprehensive Guide for 2025
FAQs
What are the benefits of artificial intelligence?
Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances efficiency, automates repetitive tasks, improves decision-making, enables advanced data analysis, and fosters innovations in various fields like healthcare, finance, and transportation.
How AI is useful in our life?
AI improves daily life by powering virtual assistants, personalizing recommendations, enhancing security through facial recognition, optimizing travel routes, and enabling smart home devices.
What is AI used for today?
Today, AI is used in healthcare for diagnostics, finance for fraud detection, customer service via chatbots, autonomous vehicles, personalized marketing, and language translation.
Who is the father of AI?
John McCarthy is often regarded as the father of AI for coining the term “artificial intelligence” and his pioneering work in the field.



















![8 Generative AI Apps to Boost Your Productivity [+2 Bonus Apps] 18 Generative AI Apps to Boost Your Productivity](https://www.guvi.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/10-Generative-AI-Apps-to-Boost-Your-Productivity.png)






Great article! I completely agree with your balanced view on AI. It’s impressive how AI reduces human error and enhances decision making, yet we must also address its ethical concerns and potential job displacement. Your comprehensive guide is both insightful and informative, offering a well-rounded perspective on the benefits and challenges of AI. Well done!!